GALLERY
PUBLICATIONS/PREPRINTS
Banerjee S et al. (2020) Semantic segmentation of microscopic neuroanatomical data by combining topological priors with encoder–decoder deep networks. Nat Mach Intell. 2020;2(10):585–594. [Link]
BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network (BICCN). A multimodal cell census and atlas of the mammalian primary motor cortex. Biorxiv. 2020;2020.10.19.343129. [Link]
Matho KS et al. (2020) Genetic dissection of glutamatergic neuron subpopulations and developmental trajectories in the cerebral cortex. Biorxiv. 2021;2020.04.22.054064. [Link]
Muñoz-Castañeda R et al. (2020) Cellular Anatomy of the Mouse Primary Motor Cortex. Biorxiv. 2020;2020.10.02.323154. [Link]
Tward D et al. (2020) Solving the where problem in neuroanatomy: a generative framework with learned mappings to register multimodal, incomplete data into a reference brain. Biorxiv. 2020 Mar 22;39:2020.03.22.002618. [Link]
Wang D et al. (2020) Detection and skeletonization of single neurons and tracer injections using topological methods. Arxiv. 2020 Mar 20;cs.CV. [Link]
ABOUT
The goal is to generate brainwide maps of cell-type specific long-range connectivity, establishing a quantitative approach to the study of cell-type distribution and connectivity in the mouse brain. These maps will thus specify the inputs and outputs of neuronal and glia populations in every brain region, corresponding to brain compartments defined in classical neuroanatomy.
To determine the cell-types of a brain region, reporter mice expressing Cre (or Flp)recombinase “tag” from cell-specific marker genes are used. The current list of such reporter mice includes most of the major known cell types in the brain and additional mice for more specialized subtypes are being generated based on advanced transcriptional profiling and the use of intersectional strategies combining two cell-marker genes. In addition, anatomical connections of the tagged cell populations can be mapped by recombination-dependent vectors for anatomical tracing, including transsynaptic labeling. In summary, it is now possible to study the function and anatomy of cell types in the mouse brain at an unprecedented spatial and temporal resolution. The whole brain is then sliced thinly, and each slice is digitally imaged. These 2-D images are reconstructed in 3D. This procedure is repeated identically, to account for individual variability.
This project provides the means to measure the numbers and ratios of specific cell types per brain areas during the critical time when neuronal circuits come together to initiate brain functions. This work will also reveal the extent to which programmed cell death of specific types is part of circuit wiring and pruning in specific brain areas. In order to accumulate data from different mice (each of whom has a slightly different brain shape and size), 3-D spatial normalization is performed using registration algorithms.
DATASETS
BICCN – Huang U19
Technique: Anterograde tracing
Background strain: C57Bl6/Agouti/Swiss
Modality: STPT
Grant number: 5U19MH114821

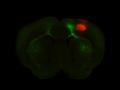
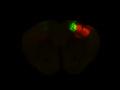
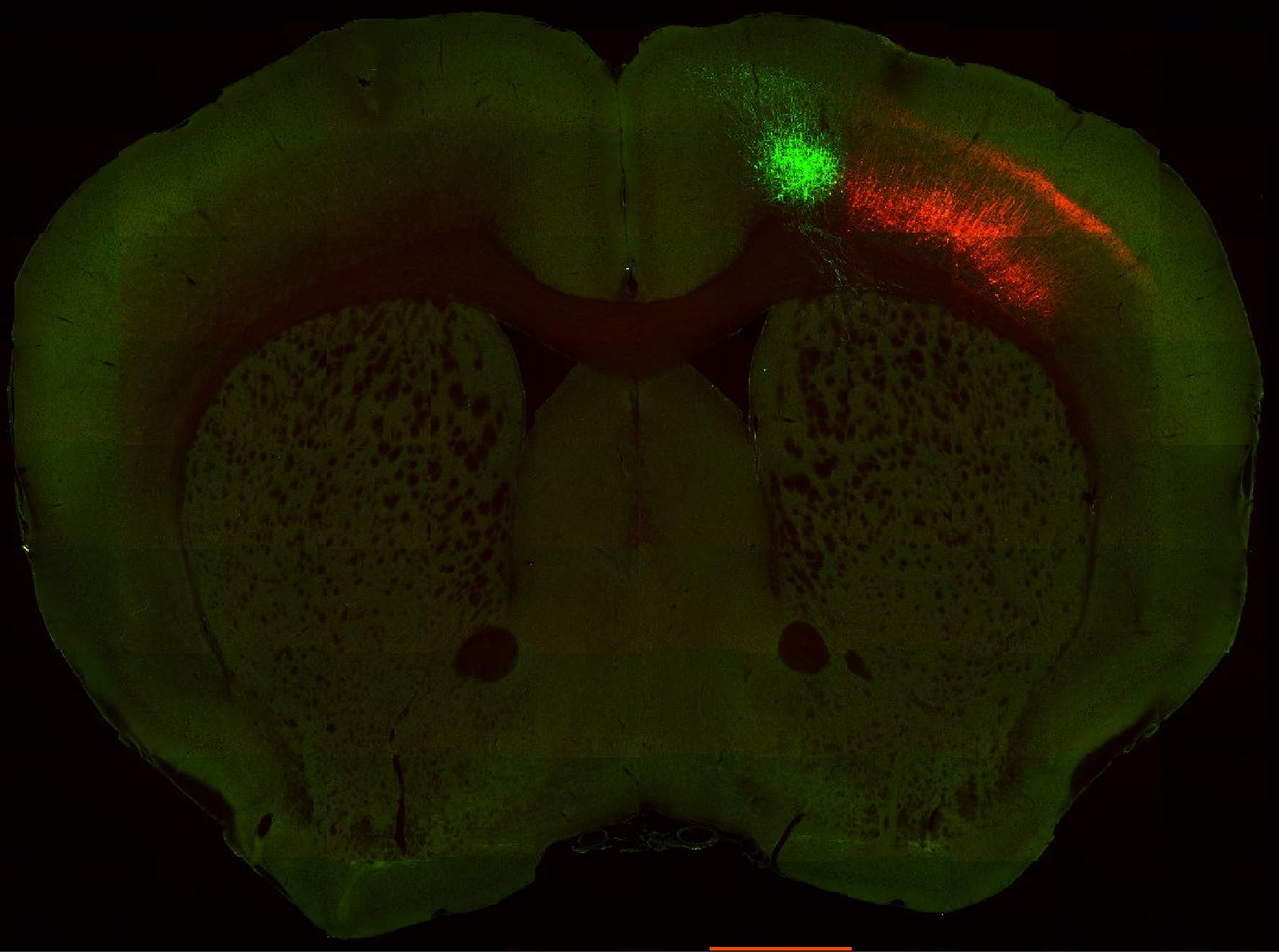 Injection in MOs and MOp Layer 6
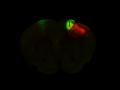
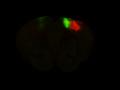
Injection in MOs and MOp Layer 6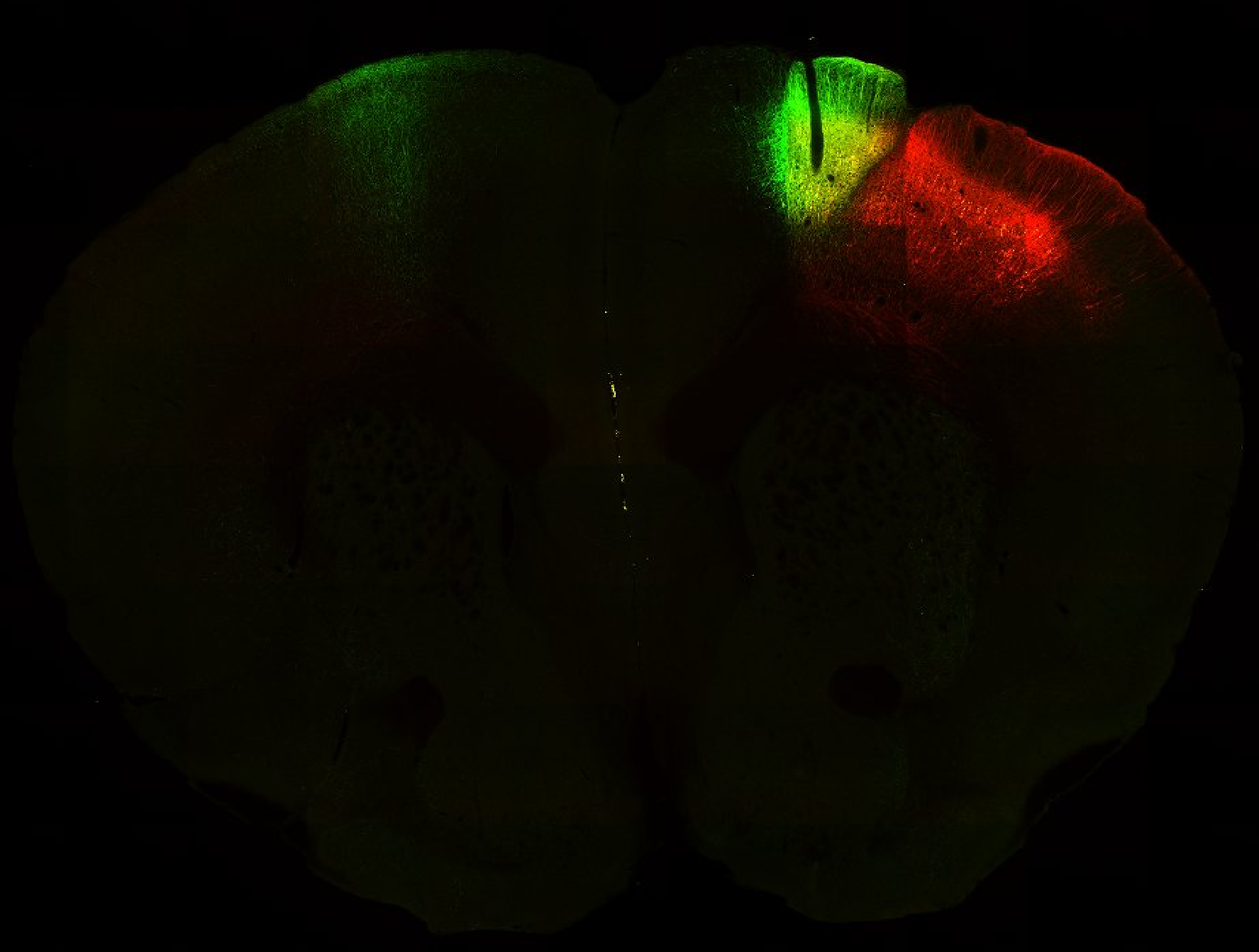 Injection in MOs and MOp Layer 5
Injection in MOs and MOp Layer 5